المطر معلومات حيوية للقطاعات الزراعية، وأقسام الأرصاد الجوية، وحتى المزارعين الفرديين. كمية الأمطار تحدد ما إذا كان على المزارعين ري محاصيلهم، وتستخدم وكالات الأرصاد الجوية بيانات الهطول لصدور تحذيرات الفيضانات.
من الواضح أن المطر يلعب دورًا مهمًا في حياتنا، لكن هل تعرف كيف يتم قياسه؟
اليوم، سأقدم طرق قياس المطر، بما في ذلك بعض العدادات الشائعة الموجودة في السوق ومبدأ عملها. آمل أن توفر هذه المقالة لك رؤى مفيدة!
قبل الغوص في المحتوى الرئيسي، اسمحوا لي أن أقدم لكم عدادات المطر من يانتاي. لقد تخصصنا في مستشعرات الأرصاد الجوية لأكثر من 13 عامًا. منتجاتنا معروفة في الصناعة بـ"دقتها العالية واقتصاديتها"، مما حصل على اعتراف واسع النطاق!
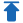
أنواع عدادات المطر
بالنظر إلى صور عدادات المطر أعلاه، قد تتساءل: إذا كانوا جميعًا يقاسون المطر، فلماذا يبدو شكلهم مختلفًا؟
هذا لأنها تعمل بناءً على مبادئ مختلفة. أدناه بعض الأنواع الشائعة لمقاييس الأمطار وكيفية عملها.
كيف يقيس مقياس المطر البصري هطول الأمطار؟
يكتشف مقياس المطر البصري القطرات باستخدام أشعة تحت حمراء أو ليزر. عندما تسقط القطرات، فإنها تشتت أو تحجب الضوء. يقوم المستشعر بتحليل التغيرات في الضوء لتحديد عدد وحجم قطرات المطر، وبالتالي حساب كمية هطول الأمطار وشدتها.

كيف يقيس مقياس المطر الكهروضغط هطول الأمطار؟
يستخدم مقياس المطر الكهروضغط مواد كهروضغاطية، والتي تولد إشارات كهربائية تحت الضغط. عندما تسقط قطرات المطر على سطح المستشعر، فإنها تنشئ نبضات كهربائية صغيرة. من خلال عد هذه النبضات وتحليل شدتها، يمكن تحديد كمية هطول الأمطار وطاقة قطرات المطر.

كيف يقيس مقياس المطر ذو الوعاء الدوار هطول الأمطار؟
يتدفق ماء المطر عبر م funnel إلى دلو صغير يميل. بمجرد أن يجمع الدلو كمية معينة من الماء (على سبيل المثال، 0.2 مم من هطول الأمطار)، فإنه يميل، ويفرغ الماء ويشغل العداد. يتم حساب إجمالي هطول الأمطار بناءً على عدد مرات ميلان الدلو.

كيف يقوم أسطوانة قياس المطر بقياس هطول الأمطار؟
يتم جمع ماء المطر في أسطوانة مقسمة باستخدام م funnel. يتم قياس مستوى الماء يدويًا في فترات زمنية منتظمة باستخدام كوب قياس. يتم تحديد كمية هطول الأمطار (بالملليمترات) بناءً على مساحة القاطع العرضي للأسطوانة. وعلى الرغم من بساطته وموثوقيته، يتطلب هذا الأسلوب التشغيل اليدوي.
كيف تقيس الصناعات المختلفة هطول الأمطار
تعد بيانات هطول الأمطار ضرورية في مختلف الصناعات، لكن القطاعات المختلفة لديها تفضيلاتها عند اختيار أدوات قياس المطر:
محطات الأرصاد الجوية: غالبًا ما تستخدم أجهزة قياس المطر البصرية لأنها لا تتطلب صيانة وتقدم دقة عالية.
الزراعة: يفضل المزارعون مقياسي الأمطار بنظام الدلو المائل لأنه يقدم توازنًا بين الدقة والكفاءة التكلفة.
الهيدرولوجيا ومصادر المياه: يُستخدم مقياس الأمطار بنظام الدلو المائل والمقياس الزلزالي على نطاق واسع في هذا المجال بسبب استقرارهما وموثوقيتهما.

التحديات في قياس هطول الأمطار
عوامل البيئة
إذا تم وضع مقياس للأمطار في مكان غير مناسب، مثل تحت الشجرة أو في منطقة رياح، فقد تتأثر دقتها. على سبيل المثال، قد تمنع الأوراق هطول الأمطار، أو قد تسبب الرياح القوية توزيعًا غير متساوٍ للمياه.
ال-Calibration والصيانة
إن الصيانة الدورية والت headlining ضروريان، خاصة لمقياس الأمطار بنظام الدلو المائل، الذي قد يتراكم فيه الحطام داخل الدلو، مما يؤثر على دقة البيانات.
بهذا ينتهي المقال! الآن أصبحت تعرف كيف يتم قياس هطول الأمطار. إذا كنت مهتمًا بمقياسي الأمطار لدينا، فلا تتردد في التواصل معنا للحصول على المزيد من المعلومات!
القراءة الموصى بها
هل هناك فرق بين مقياس الأمطار ومستشعر الأمطار؟
كيفية قياس هطول الأمطار؟ تحتاج إلى مقياس أمطار!
كيفية وضع مقياس المطر للحصول على بيانات دقيقة عن الهطول المطري

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 FR
FR
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 TH
TH