In agriculture, meteorological research, and daily life, accurately measuring rainfall is crucial. Want to know how to measure rainfall? Using a rain gauge is one of the most reliable methods. Whether it's a traditional manual rain gauge or a modern high-precision rain gauge, they can help us accurately understand rainfall conditions, allowing us to make more scientific decisions.
What is a Rain Gauge? How to Accurately Measure Rainfall?
What is a Rain Gauge?A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of precipitation over a period of time. A rain gauge typically consists of a container that collects rainwater and a scale ruler for visually reading the rainfall amount. The unit of measurement is typically millimeters (mm), representing the depth of precipitation per square meter of ground.
Depending on the measurement method and technical features, rain gauges can be divided into the following types:
Standard Rain Gauge: The most common type, consisting of an open container, suitable for personal and amateur meteorological observation.
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge: Utilizes a tipping bucket structure to record rainfall, with data automatically collected, widely used in weather stations and agricultural monitoring.
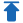
Piezoelectric Rain Gauge: Measures rainfall by detecting electrical signals generated by raindrops hitting piezoelectric sensors, suitable for precise precipitation monitoring.
Optical Rain Gauge: Uses laser or infrared technology to detect raindrop size and speed without physical contact, ideal for high-precision remote monitoring.
Multi-parameter Rain Gauge: Combines temperature, humidity, wind speed, atmospheric pressure, and other meteorological parameters for more comprehensive environmental monitoring.

How to Properly Use a Rain Gauge to Measure Rainfall?
To obtain accurate rainfall data, using the rain gauge correctly is crucial. Here are a few key steps:
Choose the Right Location for the Rain Gauge
Place the rain gauge in an open, unobstructed area to avoid interference from buildings, trees, etc.
Ensure the rain gauge is kept level to prevent measurement errors from tilting.

Observe and Record the Rainfall Measured by the Rain Gauge
For a standard rain gauge, read the scale value after the rain stops and record the millimeter reading.
The tipping bucket rain gauge automatically records data, which can be read directly from the device.
Piezoelectric and optical rain gauges are suitable for more precise data collection and can be integrated with remote monitoring systems for automated management.
Regularly Clean and Maintain the Rain Gauge
Clear leaves, dust, and other debris from the rain gauge in a timely manner to ensure accurate data.
Check whether the rain gauge is damaged or tilted to avoid affecting the measurement.

Comparison of Advantages Among Different Types of Rain Gauges
With the development of technology, high-precision devices such as tipping bucket rain gauges, piezoelectric rain gauges, and optical rain gauges are increasingly preferred by professionals. Compared to traditional rain gauges, these new types offer the following advantages:
Automatic data recording, eliminating the need for manual readings and reducing errors.
Remote rainfall monitoring, allowing real-time rainfall data to be viewed via mobile phone or computer.
High-precision sensors, such as piezoelectric and optical technologies, providing more accurate rainfall data.
Long-term data storage, facilitating weather trend analysis.
Multi-parameter monitoring: some rain gauges can also record atmospheric pressure, wind speed, and other meteorological factors.

What to Consider When Purchasing a Rain Gauge?
When choosing a rain gauge, consider the following factors to determine which one best suits your needs:
Usage Scenario:
For personal or household meteorological enthusiasts: a standard rain gauge is sufficient.
For agriculture and meteorological stations: a tipping bucket rain gauge is more practical.
For remote monitoring needs: a piezoelectric rain gauge or optical rain gauge is more convenient.
For comprehensive meteorological monitoring: a multi-parameter rain gauge provides more complete data.

Measurement Accuracy:
For high-precision data, it is recommended to choose a piezoelectric rain gauge or optical rain gauge.
For general precipitation monitoring, a tipping bucket rain gauge or standard rain gauge is sufficient.
Installation and Maintenance:
Choose a rain gauge that is easy to install and maintain, reducing the operational burden.
Optical rain gauges, which have no mechanical parts, have lower maintenance costs.

Yantai Rain Gauge
Our rain gauges are well-known for their accuracy. If you need a compact and precise rain gauge, you can choose the XF100A optical rain gauge or the XF100 piezoelectric rain gauge. If size is not a concern, you can also select the more precise tipping bucket rain gauge, although it requires maintenance!
Of course, we also offer more multi-parameter meteorological instruments that monitor other factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and atmospheric pressure, in addition to rainfall.
If you're interested in this, feel free to contact us!
Rain gauges are effective tools for measuring rainfall. Whether for agricultural planting, weather monitoring, or daily precipitation recording, they provide accurate data. By choosing the right rain gauge and mastering proper measurement methods, you can gain a more scientific understanding of rainfall, improving both production and life quality. If you are looking for high-precision, intelligent rain gauges, consider modern devices such as tipping bucket rain gauges, piezoelectric rain gauges, optical rain gauges, or even multi-parameter rain gauges for comprehensive meteorological monitoring to make measurement more convenient and efficient!
Do you have any questions about measuring rainfall?If you have any questions about how to measure rainfall or choose a rain gauge, feel free to contact us!

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 FR
FR
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 TH
TH